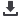
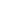
The main elements of the Single Supervisory Mechanism
129
5.2.2.2 Professional secrecy
Professional secrecy is governed by
Article 4
providing for the following rules:
(a)
Members of the Supervisory Board, the Steering Committee and any
substructures established by the Supervisory Board, ECB staff and staff sec-
onded by participating Member States carrying out supervisory duties are re-
quired not to disclose any information covered by the obligation of professional
secrecy and are subject to the ECB ConÀdentiality Regime, even after their
duties have ceased.
The term ‘ECB ConÀdentiality Regime’ is deÀned in
Article 2, point (4)
as meaning
the ECB regime which deÀnes how to classify, handle and protect conÀdential ECB
information.
In addition:
(i)
Persons having access to data covered by EU legislation imposing an obli-
gation of secrecy must also be subject to such legislation.
(ii)
The ECB must subject individuals who provide any service, directly or
indirectly, permanently or occasionally, related to the discharge of su-
pervisory duties, to equivalent professional secrecy requirements by
means of contractual arrangements.
(b)
The rules on professional secrecy contained in the
CRD IV
apply to the
above persons. In particular, conÀdential information received in the course of
their duties may be disclosed only in summary or aggregate form in such a way
that individual credit institutions cannot be identiÀed, without prejudice to
cases treated under criminal law. Nevertheless, if a credit institution has been
declared insolvent or is being compulsorily wound up, conÀdential information
not concerning third parties involved in attempts to rescue it may be disclosed
in civil or commercial proceedings.
(c)
These rules do not prevent the ECB’s supervisory function from exchanging
information with other EU or national authorities in line with applicable EU law.
5.2.2.3 Access to information between policy functions and
classiÀcation
Article 5
lays down three (3) general principles for access to information be-
tween policy functions and classiÀcation:
(a)
Information may be exchanged between the policy functions, provided
that this is permitted under relevant EU law and notwithstanding
Article 4
.